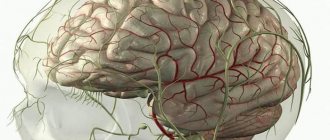
General concept
American scientist Paul McLean first used the term limbic system in 1952. Physiology received a concept for further study of the work of biological organisms at various levels.
The formation of the system occurs through communication through the mesolimbic pathway and includes an interacting chain of elements:
- the inferior and medial plane of the hemispheres of the medulla oblongata;
- nuclei of the subcortical center of visual perception (thalamus);
- anatomical system of the terminal nucleus - striatum;
- ventral region of the intermediate region.
The structure regulates emotions, creates motivation, coordinates endocrine activity and autonomic processes. The operation of the system involves the lobes of the anterior section, posterior section, diencephalon and midbrain. This includes the olfactory system; the morphofunctional association includes the dentate gyrus and the seahorse (hippocampus). The functioning of the structure involves the transparent septum of the brain region, two walls of the lateral ventricles and a collection of gray matter in the form of the basal ganglia.
The diencephalon system includes the main systems:
- leash triangle with a bunch of neurons (habenular nuclei);
- the thalamus in the form of a paired formation with a ventricle located between the nuclei;
- regulatory center hypothalamus;
- lateral and medial nuclei of the mastoid bodies.
In total, there are 12 departments in the structure, although the initial scientific developments indicated that the limbic complex is responsible for coordinating the sense of smell. All neural systems are connected to the cerebral cortex through dense ring-shaped connections.
Characteristics of system functions
The paralimbic regulatory complex receives information about the state of the body organs and external influences on the body, as a result, somatic and autonomic coordination is triggered. The system ensures adaptation to external conditions and the correct functioning of biological processes in the body.
The limbic system coordinates various directions; its functions include the following:
- the hypothalamus regulates the functioning of body organs;
- motives of behavior are formed, certain emotions arise, accompanied by movements;
- complex instincts are organized, for example, protective, sexual, nutritional;
- reactions of attention and alert reflexes appear;
- learning and memorization of events occurs using the method of long-term, short-term and spatial fixation in the brain;
- smells are recognized;
- shows interest in research activities and the ability to navigate the terrain;
- communicative speech or simple sounds are organized;
- there is a change in periods of wakefulness and falling asleep.
Deprivation of the unified system of individual participating structures leads to inertia in psychological terms. Excitation of the complex causes hyperactivity. When the amygdala is stimulated, anger begins to appear. The system coordinates actions related to the search for food and satiation, and activates the danger response.
The structure, when interacting with the hormonal complex, regulates complex actions and plays the role of coordinator of the body’s behavior. The aggregate influences life activities by coordinating the work of the neural autonomic system. Sensory-hormonal work in the body of animals and humans cannot obey brain commands, but depends on the mutual connection of the emotional and limbic structure.
Importance in memory organization
The main function is to coordinate activity with the memorization mechanism. Science associates short-term memory with the hippocampus, and long-term memories are recorded with the assistance of the neocortex. The manifestation of experience, personal skills, abilities and knowledge is used by the body through the action of the limbic system. In this case, a hormonal-sensual stimulation of the brain occurs, which requests a store of knowledge from the neocortex.
The functions of the system include the explanation and interpretation of emotional reactions, the preservation of memorable events and ways of possibly responding to external conditions.
In recent years, scientists have added demonic areas to the association:
- paraphthopacambine gyrus;
- subcortical formations;
- frontal medial cortex;
- orbitofrontal region of the surface of the brain.
The system does the work of activating verbal memory about events and acquired practices. All directions are determined by the ability of cells to accept signs of an electromagnetic, chemical and mechanical nature.
The source of signals can be not only the external environment; shocks are also supplied by the internal nervous system. A change in the well-being of the effector system leads to a physical transformation of the visible behavior pattern.
Formation of emotions
The action of the hypothalamus is more pronounced in relation to emotional outbursts than in the generation of affective feelings. The manifestation of material symptoms of arousal by another individual is sometimes threatening, so the signal returns to the limbic centers (anterior nuclei) through the hypothalamus and increases the feeling of anxiety.
A negative biological mechanism sometimes manifests itself so clearly that it accumulates a panic situation. Knowledge and understanding of this phenomenon is important in clinical and therapeutic terms.
The limbic system of the brain is responsible for many activities. Its structure and functions determine the directions of practice:
- endocrine;
- motivational;
- sensual;
- vegetative.
The septum pellucidum, like the amygdala, is involved in processing various information that comes from the olfactory organs. The amygdalus helps create feelings of pleasure and sexual arousal, and the acuity of perception varies depending on the activity and maturity of the body.
In the early days of research, it was widely believed that the limbic connections worked exclusively with the sense of smell, but in animals without a developed sense of smell, the system also evolved. Most of all, the network of interaction between traditional limbic associations and the cortex of the main cerebral hemispheres develops in humans. Some symptoms of attachment appear in birds and mammals, but are almost absent in reptiles, amphibians and other previous species.
Substances involved in the formation of emotions:
- norepinephrine;
- dopamine;
- serotonin.
Neurotransmitters are synthesized in sufficient quantities by brain secretions and provided to the limbic complex for work. If the natural balance in composition between these substances is disturbed, resonance occurs, and mental and nervous diseases appear.
Action without worries
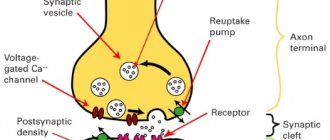
Limbic formations are elements of the structure of integrative centers for coordinating the autonomic system in the body. The neurons of the complex receive impulse signals from the subcortical nuclei, cortex, hypothalamus (region in the intermediate section of the brain), thalamus (gray matter at the top of the intermediate section), reticular formation along the trunk, and body organs.
A characteristic feature of the system is the presence of strong neural interactions for the joint operation of many brain structures. The limbic complex is involved in the processes:
- afferent synthesis (extracting information from parts of the brain to satisfy needs);
- regulation of brain electrical activity;
- coordination of metabolic processes;
- adjustments to the functioning of internal organs, secretory glands, and the condition of lymphatic and blood vessels.
An irritant effect on individual system elements contributes to the manifestation of protective behavior and changes in the functioning of organs within the body. The limbic system strives to maintain a stable internal environment called homeostasis. This includes regulating metabolism, producing essential enzymes and controlling their activity.
Consciousness and unconsciousness. Higher intelligence. Three Minds Model
The Three Minds model was simply and clearly formulated by world-famous coaches, the creators of the third generation school of transformational coaching - Stephen Gilligan and Jack Makani. In turn, they relied on the latest achievements of science in the study of the conscious and unconscious, as well as the collective experience of world religions.
In all world religions there is the idea that a person has three aspects of consciousness, or let’s call them three minds.
Let's call the first mind the Conscious Mind .
The second is the Unconscious Mind .
And the third - by the Higher Mind .
And let’s agree that these three minds are three aspects of any personality.
If you look at the picture at the beginning of this article showing the structure of the brain and look for where our three minds reside, it looks like the Conscious Mind and the Higher Mind are located in the neocortex.
And the Unconscious wanders between the reptilian and limbic brain, from time to time sending signals to the neocortex, where the Higher and Conscious minds are located, in the form of images, sounds, feelings and bodily sensations.
And two more very important observations:
- The higher mind resides not only in the neocortex of a particular person, but is somehow connected to the field of the collective unconscious beyond the individual person.
- The Higher Mind and the Conscious Mind do not communicate directly. They ALWAYS interact through the Unconscious. This is why a person has psychological problems. But we'll talk about this a little later.
Now let's try to sort out the areas of responsibility of our three minds.
Shelves are, of course, a metaphor convenient for talking about such complex matters as our conscious, unconscious and spiritual.
So, what is our Higher Mind responsible for?
For ideas, foresight, values, meaning, spirituality, self-control.
It seems that the Higher Mind of each person has a special task regarding the life of a person.
This task can be called a mission or purpose. This most important task in life is closely related to deep identity, the awareness of who I am, and without which my life has no meaning.
The higher mind is the wisest part of us, which is responsible for vision of life's path, inspiration and access to special resources of collective experience.
What is under the control of the Conscious Mind?
Perception of reality, that is, those images, sounds, bodily sensations, internal dialogues that we are aware of.
Rational and logical thinking.
Making informed decisions.
The unconscious is a giant repository of everything, everyone, everyone
events that have ever happened to us,
emotions we've ever felt
the decisions we made
internal and external conflicts,
beliefs and principles,
physiological processes in our body.
How do Consciousness, the Unconscious and the Higher Mind interact with each other?
Remember, we have already said that the Higher and Conscious minds do not interact directly, but necessarily through an intermediary - the Unconscious.
And as we remember, everything, everything, everything is stored in the sphere of the Unconscious, including all our grievances, fears, sorrows and pains, all our limiting beliefs.
All this garbage, frozen in its original form, accumulated over the years, affects our lives.
Creates tensions and diseases in our body.
Cuts scars on our emotions.
It clouds our states.
It creates traffic jams and stagnation in our thoughts and actions.
Silences the call of our true values and important life goals.
And in order to develop and achieve what we want, it is important for us from time to time, or better yet, to regularly get rid of garbage in the unconscious. And to do this, be able to organize teamwork between three minds.
A professional coach helps in organizing such teamwork of minds. This is the essence of his work.
Operational disruptions
Patients develop amnesia due to changes in the limbic structure, traumatic head injuries, or natural defects. The neural interaction complex is not considered as a place for storing information. The system is designed to combine different parts of memory and reproduce the required moments when necessary.
Disturbances in the functioning of the system do not destroy short or long-term memories, but destroy the logical connection between them and do not make it possible to consciously repeat them. In this version, different pieces of information are stored and guarantee the functioning of procedural memory. Korsakoff's syndrome in psychology allows the patient to fully remember all past events, but patients cannot learn and remember new information.
Hypothalamic syndrome is observed when there is a range of vegetative, endocrine disorders caused by pathological changes in the hypothalamus. At the same time, body weight increases, headaches, and mood swings appear. Progressive changes in the functioning of the organ lead to partial or complete loss of the ability to work, and reproductive health is impaired.
Alcohol contributes to the occurrence of persistent disorders of the thalamus. In this case, memory for recent incidents suffers, for example, the patient cannot remember the dishes for breakfast and does not even have the feeling that he had breakfast. Such people reproduce events from their youth or childhood with extraordinary accuracy.
Studies on monkeys led to the conclusion that after removal of the anterior temporal tonsil, the animals showed hyperactivity, increased emotionality, fearlessness, and put foreign objects into their mouths. The animals did not recognize familiar objects, since part of their limbic complex was removed.
The left amygdala is responsible for social phobia, impulsive activity, determines recovery from traumatic stress, and the removal of excessive anxiety. Enlargement of the organ leads to a borderline disorder of consciousness; patients have difficulty distinguishing emotions on the faces of people around them. Manic and depressive notes in behavior were observed with a decrease in the gland.
Limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM - emotional brain, responsible for territorial issues, creating a common space, conflicts and showdowns, establishing and maintaining boundaries.
Operates on the principle:
- giving - accepting;
- receiving - giving.
The limbic system has its pros and cons. The good news is that the system teaches a person empathy, the ability to understand what is happening to another person.
The bad news is the function of fusion, when a person dissolves into others, losing himself.
The emotional brain is engaged in assessing emotional significance, learning to recognize the context of information from the world.
The main causes of psychosomatic conditions with which people come to therapy are at the level of unconscious generic programs formed at the level of the limbic system - they relate to emotional boundaries and the boundaries of self-determination.
At this level, biological programs are basic, but unconscious generic programs implemented in social life are already included. People often say “I'm insecure”, “I don't know who I am”, “I'm lazy” and so on. These are also problems of self-realization and building personal relationships. The social aspect is implemented from the age range from approximately 3 years to 8 years.
This level shows (what they were) and determines (what they will be) relationships in the family, the relationship between a man and a woman in generic relationships.
For example, a child was rejected in childhood, often denied communication, and left alone. His childhood included many experiences of suffering, and his limbic system developed programs of abandonment and rejection.
The child has grown up and become an adult. He will unconsciously reproduce childhood traumas in the present in order to suffer, or he will react to any unpleasant situation according to the above-mentioned principle of “being upset” - this is how he learned . And he will be a hostage to his childhood trauma until he begins to track these unconscious reactions and begins to learn to change and realize them, at the level of behavior and emotional response.
Relief of condition
The prognosis of dysfunction of the limbic complex depends on the severity of the disorder. There is a possibility of complete recovery with minor deviations, but sometimes the disease begins to progress.
Complications arise in the form of:
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- development of obesity in the final stages;
- the appearance of infertility.
Pathology of the limbic structure is found in the practice of endocrinologists, neurologists, and gynecologists and causes certain difficulties in diagnosis, since the symptoms resemble manifestations of underlying diseases.
With the development of new technologies, in particular MRI, doctors have the opportunity to identify disorders of the hypothalamus or amygdala at the initial stage and begin treatment in a timely manner. For this purpose, antidepressants and other psychological drugs are used, which cannot be used independently.
To alleviate the mild severity, a healthy lifestyle and regular exercise are recommended. Sport increases blood circulation and nutrition of brain tissue, and therefore improves the functioning of the system. Exercises for the upper body, such as push-ups and arm swings, work effectively. Light relaxing massages are performed to deliver nutrients and oxygen. It is recommended to eat a diet high in animal proteins, fiber and limiting simple carbohydrates to increase the level of neurotransmitter synthesis.