Prostate function in men
The prostate is a gland of the male genital organs, its main function is to secrete sperm fluid that nourishes, dilutes and protects sperm. The prostate muscles help push semen into the urethra during ejaculation. The fluid produced by the prostate, together with sperm (sperm cells from the testicles) and secretions of other glands, forms sperm.
The functional state of the prostate gland can be determined by its size
The size of the prostate is closely related to the health of the male body. But without special studies, taking into account only the amount of ejaculate, it is not possible to calculate the volume of the prostate. Only by finding out the size of the organ itself can you calculate the volume of the prostate gland to determine its health.
Where is the prostate located?
The prostate is located between the bladder and the root of the penis. This gland is located in front of the rectum. The urethra (urethra) runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, this “tube” serves to remove urine from the body.
To get the actual volume of the prostate gland, the formula is taken from a school mathematics course: the length is multiplied by the height and width of the organ. The resulting product is multiplied by the corresponding coefficient, which allows you to calculate the volume of ellipsoidal bodies.
Before determining deviations, you should know the standard indicators. So, the average weight of a normal prostate in adult men is about 11 grams, with deviations ranging from 7 to 16 grams. The round shape and size of the iron resembles a walnut among the sizes.
Structure and functions of the prostate gland
The prostate gland is the most important endocrine organ of the male genitourinary system.
Impaired functioning of the prostate leads to a deterioration in sexual life and weakened reproductive health.
The prostate is an internal secretion organ formed by two lobes connected by a thin strip of tissue.
The gland is a complex alveolar-tubular organ, has an elastic and dense structure, and is trapezoidal in shape.
The ducts of the gland exit into the urethra. The back wall of the prostate is adjacent to the intestine, so the doctor can easily feel the gland by entering the patient’s rectum with his fingers.
The main function of the organ is the synthesis of a secretion that dilutes sperm. The secretion contains vitamins, enzymes, antibodies, and microelements.
The gland also closes the urethra during erection. The activity of the prostate is regulated by hormones secreted by the pituitary gland.
The prostate is a capricious organ; in men 40–60 years old it causes many problems. Prostate volume changes throughout life and is determined by numerous external and internal factors.
The size of the prostate gland is usually determined by the man’s age, hormonal levels, and the general condition of the body. In men over 50 years of age, the tissue connecting the lobes of the prostate begins to grow, gradually squeezing the bladder and urethra. This painful phenomenon is called prostate adenoma.
Normal prostate size
The normal prostate gland measures approximately 3 × 3 × 5 cm or a volume of 25 ml. We see that the formula of simply multiplying the length, width and height will not yield a 25-ml prostate volume, because the shape of the prostate is far from a geometrically regular rectangle. For an accurate calculation, a coefficient is used, which we will discuss later.
Various prostate measurements (mean ± standard deviation)
| Age | Group 1 (40–49 years old) | Group 3 (60–70 years old) |
| Length (mm) | 37,55 ± 4,27 | 41,13 ± 6,18 |
| TZW (Transitional Zone Width), mm | 30,25 ± 4,84 | 34,21 ± 7,08 |
| Height, mm | 21,64 ± 3,73 | 25,02 ± 6,07 |
Using age ranges when diagnosing prostate cancer helps avoid unnecessary testing in older men with naturally larger glands (about the size of a large walnut).
Why does the prostate enlarge?
There are benign (noncancerous) enlargements of the prostate that block the normal flow of urine through the urethra. Inside the prostate, cells gradually grow and begin to increase the parenchyma of the organ. They put pressure on the urethra, through which urine and semen are released. When the parenchyma begins to enlarge, it gradually compresses the urethra and can lead to a complete blockage of the urethra.
Diagnostic ultrasound shows an increase in the volume of the prostate gland very well. Modern devices allow you to obtain high-resolution three-dimensional images. Next, the volume of the prostate gland is calculated using ultrasound and it is decided whether it is worth starting treatment, whether it makes sense to buy the same Smartprost physiotherapeutic device and take other measures.
The role of estrogen
Estrogen has also been linked to prostate enlargement. As men age, less testosterone is produced in the blood, which leads to an increase in the relative proportion of estrogen. This female hormone provokes a change in the appearance of men, many feminine characteristics appear.
What diseases are hidden behind an increase in the permissible size of the prostate?
An increase in the linear dimensions of the prostate is characteristic of most pathological conditions of the organ, from banal prostatitis to oncological transformation of prostatic tissue.
Prostatitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of infectious or non-infectious origin, which is accompanied by the following symptoms: pain in the pelvic area, reproductive dysfunction, increased organ size, problems with urination. From the editor: Prostatilen suppositories: dosage, composition, instructions for use, indications and contraindications
Prostatitis can develop against the background of microbial damage to soft tissues, physical inactivity, venous stagnation, hypothermia or irregular sexual activity. If the disease is not diagnosed and treated in time, prostatitis can spread to the kidneys and significantly impair their function, as well as cause impotence and infertility.
Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor in which the size of the organ increases several times. The disease leads to impaired urinary function and deterioration of erection.
Adenoma occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance and age-related changes in the thickness of the prostate. It is accompanied by intense pain and the appearance of symptoms of acute dysuria. If the disease is not treated, the gland will continue to increase in size and worsen the patient's general condition.
A prostate cyst is a rare disease that is accompanied by the formation of a formation with serous content in the thickness of the organ.
As a result of the growth of the cyst, the gland becomes enlarged. The cyst causes dysuria, reproductive dysfunction, and pain in the lower abdomen. Treatment of the formation should be surgical.
Enlargement of the prostate may be associated with the formation of stones in its thickness. This is a rather painful process, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine and ejaculate, and also leads to infertility. Prostate cancer is the most dangerous disease of the organ, occurring for a variety of reasons, including a hereditary predisposition to malignant transformation, bad habits, and eating poor-quality foods.
As the tumor increases, patients begin to complain of pain in the perineum, swelling of the extremities, impaired urine flow, and the appearance of blood in the urine.
Cancer treatment tactics depend on the stage of the disease and the presence of metastases. Such patients are indicated for chemotherapy, as well as radical surgery to remove the prostate gland.
At what age should you have your prostate checked?
After forty years, men are advised to pay attention to the condition of their prostate gland. Beginning around age 50 (or earlier if family history warrants), all men should consider regular prostate cancer screening. The first step is to donate blood to test the level of PSA - prostate specific antigen.
How often should you have your prostate checked?
If a blood test shows that the PSA level is below 1 nanogram per milliliter of blood and the doctor does not find any bad changes in the prostate, then you can not undergo a rectal examination for another 10 years. However, if the PSA is between one and two nanograms per milliliter of blood, then it is recommended to get tested every two years. The volume of the prostate is calculated using ultrasound, the formula of which reliably shows changes without additional examinations.
Symptoms of prostate enlargement
Symptoms of prostate adenoma include:
ORDER
- Weak or slow urine flow.
- Feeling of insufficient emptying of the bladder.
- Difficulty starting to urinate.
- Frequent urination.
- Frequently getting up at night to urinate.
- Intermittent stream of urine that starts and stops.
- Strained urination.
When does the pain occur?
Both prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia (growth) of the prostate gland (BPH) can cause pain. However, if BPH (formerly called an adenoma) causes pain, it usually only occurs during urination. With prostatitis, pain may appear during urination, ejaculation, or manifest itself as generalized pain in the abdomen and/or groin area.
Early signs of prostate cancer
- Burning or pain when urinating.
- Difficulty starting and stopping urination.
- Numerous urge to urinate at night.
- Loss of bladder control.
- Decreased urine volume or flow rate.
- Bloody urine (hematuria).
- Blood in semen.
And to differentiate different lesions, it is not enough to find out the volume of the prostate gland; you need to know how to calculate this indicator to determine the optimal treatment method.
Therapeutic measures
Based on the results of all necessary tests, the stage of the disease and the clinical manifestations of prostate adenoma, the doctor, together with the patient, selects the appropriate therapeutic tactics.
There are several treatment regimens for patients with prostate adenoma:
- Monitoring the dynamics of the disease, conservative medicine.
- Drug therapy.
- Surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment of prostate adenoma includes adjustments to lifestyle and daily routine. The doctor selects an individual set of physical exercises; you can use herbal preparations to improve blood circulation in the hip area. In the early stages of the development of the disease, when the gland is slightly enlarged, folk remedies such as a decoction of nettle leaves and rhizomes, pumpkin seeds, and medicinal baths can help stop the growth of prostate adenoma and alleviate its symptoms.
Nettle decoction is taken at stages I and II of glandular adenoma. To prepare it you need to take 1 tbsp. l of raw materials and pour a glass of hot water, boil for 5 minutes, strain. Take 200 ml of decoction in the morning and evening. The course of treatment is one month.
Considering that the prostate is an androgen-dependent gland, when it enlarges, low testosterone levels are often recorded. Pumpkin seeds contain a lot of zinc and other trace elements that contribute to the rapid restoration of the hormone. To satisfy the body's daily need for zinc, it is enough to eat half a glass of unroasted pumpkin seeds daily.
Sitz baths will have an anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect on the diseased gland. For these purposes, pharmaceutical preparations from chamomile flowers, oak bark, sage or marsh cudweed are suitable. Take a bath for at least 10 minutes, but no more than an hour.
It is worth noting that it is possible to treat prostate adenoma with traditional methods in situations where an increase in the size of the gland has been recently discovered, and in the absence of disturbing symptoms. If the volume of the prostate is more than 40 cm³, then it is better to turn to official medicine.
Nettle decoction is used as an adjuvant treatment in the initial stages of the disease.
Typically, prostate adenoma is treated with alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. Unlike inhibitors, the effect of which is noticeable only after 3-6 months, alpha-blockers begin to act from the first days of use. However, this feature causes adverse reactions of the body to the drug: dizziness, headache, severe tachycardia, dyspeptic symptoms. Also, adrenergic blockers slow down the enlargement of the gland, but do not stop its growth. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are used to reduce prostate volume and before surgical procedures.
Abdominal surgery is used to treat large prostate adenomas. Due to the widespread use of diagnostic methods and good awareness among men about sexual health and the symptoms of this disorder, doctors are increasingly less likely to encounter advanced stages of adenoma. Therefore, for pathological enlargement of the prostate, the “gold standard” is transurethral resection. The source of inflammation is removed using a resectoscope, which leads to normalization of the volume of the gland.
Prostate adenoma can significantly worsen a man’s quality of life. Fortunately, many years of experience in treating genitourinary diseases is a guarantee of a successful and effective solution to this problem. Be healthy!
Source egopik.ru
Prostate adenoma is a disease in which a benign tumor develops in the prostate gland. In medicine, this disease is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
How is prostate size determined?
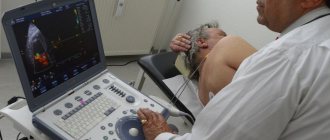
For transrectal ultrasound, patients are asked to lie on their side with their knees bent. A disposable protective cap is placed on the sensor, lubricated, and inserted into the rectum through the anus. Images are taken from different angles to get the best view of the prostate gland for accurate measurements and diagnosis.
Video: how a prostate ultrasound is performed.
An ultrasound examination of the prostate uses a finger-sized probe that is inserted a short distance into the rectum. This probe creates harmless sound waves. A person cannot hear them, but they bounce off the surface of the organ being examined. An ultrasound machine records sound waves and turns them into videos or photographs. Pictures are flat (2D) or three-dimensional, three-dimensional (3D), black and white or color. They look at the structure of the organ and the presence of nodes. The specialist looks for changes in contours and echogenicity in each zone. At the same time, a small tissue sample may be taken for biopsy.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland is more accurate than x-rays. This is because the technician can see images in real time as the probe moves across the rectum, rather than taking a photo and then examining static images. Ultrasound examinations are also safer than x-rays because the ultrasound machine does not generate dangerous radiation.
Prostate volume calculation
Urologists usually use a universal formula to calculate the volume of the gland.
It looks like this: patient’s age x 0.13 + 16.4, where 0.13 and 16.4 are special coefficients that reflect normal indicators. Thus, it is possible to determine the normal volume of the gland for any age. The main reasons for the increase in prostate volume are:
- Age-related restructuring of parenchyma cells with weakening of their functions;
- General health;
- Lifestyle;
- Hereditary factors.
In itself, a slightly increased size and volume of an organ may not mean anything. Only the clinical manifestations of this transformation become critical for health:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Increased nocturnal diuresis;
- Pain in the groin;
- Weakened erection.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland and other types of research (for example, analysis of the level of free PSA in the blood) are aimed at differentiating the usual functional failure of the organ from its beginning organic degeneration.
Formula for calculating prostate volume
The probe is moved at an angle from one side to the other. Every urologist who conducts such an examination knows how to calculate the volume of the prostate in cm3 based on the measurement results. After measuring the height and length in the sagittal plane and the width in the axial plane, the volume is calculated: the product of the three measured values is multiplied by the index 0.52.
That is, with transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), the volume is estimated using a traditional mathematical calculation of the volume of the ellipsoid based on the resulting height (H), width (W) and length (L) of the prostate.
Calculation of prostate volume formula:
H × W × L × 0.523.
Where the exact index value for calculating the volume of the prostate gland is 0.523.
How the size and condition of the prostate gland is studied
A urologist deals with treatment and preventive examinations of male organs. The first thing this doctor does is take a medical history of the patient, collecting a primary anamnesis. That is, the doctor interviews the patient in detail, records the answers and his assumptions.
The next step is palpation of the prostate gland. Thanks to this study, a good urologist is able to detect even a slight enlargement of the gland. By palpating the organ, the doctor notes whether there is pain, how elastic the tissue is, or whether there are any seals that may indicate a tumor. If the urologist has noted abnormalities, the next step for examination is ultrasound.
The normal size of the prostate gland during ultrasound can be easily distinguished from abnormalities with almost 100% probability. Modern equipment provides a clear enough image to diagnose and clarify most diseases: cysts, tumors, nodules.
Editor's note: Is it possible to have children after chemotherapy? Reproductive capacity of the body of a man and a woman after chemotherapy
The more specific the structure of the neoplasm, the easier it is for the urologist to make a final diagnosis and begin the correct treatment. A cyst is a cavity formation in the gland that is filled with fluid. Ultrasound is also excellent at diagnosing diseases such as calcifications. These are peculiar stones of oval or round shape. Their size usually does not exceed 200mm.
Before TRUS, you need to properly prepare your bowels. To do this, you can choose either an enema with warm, boiled water, or a microenema. Microclysters are very popular. They are harmless and gently relax the intestines even with severe constipation. Fecal stones dissolve, facilitating the process of defecation.
Ultrasound performed through the peritoneum of the lower abdomen does not always give a satisfactory result. For example, a large layer of abdominal fat in obese men is a huge barrier to ultrasound. Another type of ultrasound examination, TRUS, comes to the rescue.
A sensor is inserted into the patient's anus, which allows you to see the organ being examined, literally in the palm of your hand. In the attached video you can see details of how a transrectal ultrasound examination is performed, find out how unpleasant it can be and how you need to prepare before the appointment.
In addition to ultrasound examination, if tumors or malignancies are suspected, the patient undergoes an MRI. This is the most accurate device that allows you to examine the smallest changes in the volume of the prostate gland, which normally should be smaller, but the doctor cannot draw a conclusion based on ultrasound and age standards due to suspicions of cancer or a tumor.
X-rays are used less and less frequently to distinguish between a normal prostate and an enlarged one. This method of studying the size of the prostate gland is called prostatography. Since the gland stands out little in shape, texture and color against the background of other organs located nearby, a simple x-ray of this organ is ineffective.
In order to isolate the prostate, a contrast agent is injected into the empty bladder using a catheter. A healthy organ has a clear, even structure, without irregularities, spots, or neoplasms. If, during prostatography, a heterogeneous structure was identified, the diagnosis will most likely be prostate atrophy. Exceeding the normal volume of the prostate is prostatic hyperplasia.
How can you reduce the size of your prostate?
Only a doctor can correctly determine the size and calculate the volume of the prostate gland, conduct the correct examination and diagnose the disease, and then develop an effective treatment regimen. But patients can help doctors control the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. To maintain health, patients must independently:
- Limit drinks in the evening.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol.
- Limit your intake of decongestants and antihistamines.
- Go to the toilet at the first urge to urinate.
- Take a bath regularly.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Stay physically and sexually active.
- Urination should be done in two steps, after a few seconds, this is an important nuance.
Surgical treatment of the prostate
Standard surgical procedures
- TURP: transurethral (through the urethra) resection (truncation) of the prostate gland through the urethra. This procedure is the "gold standard for effective treatment of BPH."
- Open prostatectomy (complete removal of the gland for cancer).
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
This surgery is used to treat problems with urination due to an enlarged prostate gland. This is the most common surgery to treat BPH. The doctor removes only the parts of the prostate gland that are obstructing the flow of urine. A combined visual and surgical instrument (resectoscope) is inserted through the tip of the penis and into the urethra.
Every male urologist must master diagnostic techniques and know how to calculate the volume of the prostate by size. The urologist’s tasks also include determining the most optimal treatment method, incl. determining the need for surgical intervention. It is important for men to consult a doctor on time and carefully monitor their condition.
Treatment of prostate adenoma
There are several methods of treating BPH, which also depend directly on the degree of development of the pathology. Treatment of the disease is often complex: medicinal methods are combined with the use of additional alternative traditional medicine, the prescription of a special diet and physical exercises aimed at improving blood circulation and eliminating congestive processes.
Drug treatment
If the disease is at the first stage, then the pathological process can be slowed down with the help of special medications.
If the prostate has increased in size due to adenoma, then the treatment method is alpha-1-blockers such as Alfuzosin or Tamsulosin. The products improve the urinary process, eliminate inflammation and irritation in the urinary tract, and restore normal tone of the smooth muscles of the gland.
Alpha-5-reductase drugs are also prescribed to shrink the gland. The drugs help neutralize the effects of androgen hormones on the prostate gland.
To relieve pain, doctors prescribe painkillers, available in the form of suppositories and tablets.
Surgery
If the patient is diagnosed with a second or third degree of severity of adenoma, then surgical methods of therapy are often prescribed (laser vaporization, embolization of prostate arteries, microwave treatment, prostatectomy, and others).
Source vylechim-prostatit.ru