Eliminating pain
Due to the development of hematoma, fractures of the base of the skull, hemorrhage in the brain structures, contusions and other types of injuries after TBI, the likelihood of severe pain syndrome is quite high.
Along with the pain, dizziness is also often noted, which can cause double vision. Pain and dizziness can occur both in the presence of relevant factors (weather, sudden turning of the head, etc.) and in their complete absence (for example, in the morning or evening hours).
Life after a TBI with headaches worries many patients, so if you have pain, you need to consult a physiotherapist or massage therapist. Doctors can also prescribe special painkillers, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and other procedures if there are appropriate indications.
If medications and traditional procedures do not help eliminate the pain, the patient is sent for a repeat MRI or CT scan to find out what exactly is causing the pain (impaired vascular patency, hidden hemorrhages and hematomas, pinched nerves, etc.). If the pain syndrome is severe and significantly impairs a person’s quality of life, then surgery may be indicated.
Rehabilitation after head injury
Traumatic brain injuries are characterized by damage to the soft tissues and bones of the skull: fractures, bruises, concussions. Since the brain controls all life processes, head injuries lead to multiple disorders:
- loss of control over motor functions;
- loss of touch, vision, hearing, and other sensory functions;
- insomnia, attention and memory disorders, speech disorders;
- post-traumatic epilepsy, hydrocephalus;
- changes in behavior and personality, the appearance of aggression, apathy and other disorders.
Rehabilitation measures are aimed at eliminating these disorders and restoring all brain functions as completely as possible.
The set of procedures may include:
- neuropsychological correction,
- drug therapy,
- psychotherapy,
- stabilometry to improve coordination and balance,
- aquatherapy and other techniques.
Time frame for rehabilitation after head injuries
Timely initiation of physiotherapeutic procedures increases the patient's chances of a full return to normal life. The recovery process after traumatic brain injury can be divided into several periods:
- acute phase (first 3 days),
- acute phase (3 weeks),
- intermediate period.
The optimal time to start rehabilitation is one month from the moment of injury, and in the first year and a half after a TBI they are most effective in terms of recovery.
Modern approach to rehabilitation after head injuries
Today, the best rehabilitation method is considered to be a multidisciplinary approach. It is based on the comprehensive restoration of motor, adaptation, everyday life and psycho-emotional components. To achieve improvement in all these areas, a group of specialists works with the patient:
- Rehabilitation doctor: provides drug therapy and prevents complications.
- Physiotherapist: deals with the restoration of motor function by selecting individual techniques (kinesthetics, PNF, swimming pool exercises, exercise therapy and other procedures).
- Occupational therapist: helps the patient cope with usual social and everyday tasks (personal hygiene, dressing, cooking, etc.).
- Speech therapist: conducts classes to correct speech disorders.
- Neuropsychologist: corrects psychological and emotional disorders, helps fight apathy, attacks of irritability and aggression, and memory loss.
- Nurse: monitors the timely intake of medications and attendance at recommended procedures, provides patient accompaniment and care.
A comprehensive approach to rehabilitation after head injuries helps to avoid situations where the body's functions and capabilities are restored unevenly or not fully, which is why the patient continues to suffer from physical limitations or psychological discomfort. Also, parallel completion of versatile rehabilitation courses helps to make the most of the optimal time period for recovery.
Rehabilitation after head injuries at the Center for Practical Neurology
Our Center provides excellent conditions for rehabilitation procedures. We use modern rehabilitation programs to restore motor functions; our specialists have extensive experience and are ready to apply all their knowledge to solve various problems. Come for a consultation and we will create an individual rehabilitation course that will help you return to a full life in the shortest possible time.
Consequences of a concussion
In some patients, post-stress disorders may appear as possible consequences after a concussion:
- severe headaches lasting up to 2 weeks, the severity of which decreases with the consumption of analgesics or other painkillers;
- dizziness, difficulty concentrating, problems performing normal activities;
- vomiting for no apparent reason, nausea.
Often, accompanying manifestations of the lesion disappear after some time without treatment; if they bother the patient for several months, it is necessary to visit a doctor and get an appointment for a visit to a neurologist or a brain tomography to clarify the diagnosis.
Complications
Among the consequences of the injury, there are various complications after a concussion. Repeated concussions cause a disorder called boxer encephalopathy.
This is a type of parkinsonism characteristic of people who are professional boxers and periodically experience head injuries.
Post-traumatic encephalopathy is manifested by some lag in the movements of one leg or “slaps” of the foot, problems with balance, and staggering; Some patients experience clearly noticeable inhibition of actions, confusion, clearly visible dragging of the legs, specific mental abnormalities (decreased vocabulary, etc.), trembling of the head, arms and legs.
Complications after a head injury can be extremely severe, so if you have a concussion, you should immediately consult a doctor, because any such injury can cause changes in the individual’s psyche and physical impairment.
Such complications include:
- The appearance of a special reaction to drinking alcohol or infection of the body: in a drunken state, in the presence of an infectious disease, the patient experiences confusion, outbursts of overexcitation and other mental disorders.
- Disorders associated with changes in vascular tone. Typically, they manifest themselves as: persistent, constant headaches, the strength of which increases with physical activity, dizziness that appears during physical effort, alternating rushes of blood to the head and severe pallor with increased sweating, and the rapid onset of fatigue.
- Uncontrollable outbursts of emotions, increased irritability, rapid agitation, falling into rage, often with an aggressive attitude towards others. Quite often, aggressive outbursts are followed by repentance, and the patient is ashamed of his behavior.
- Manifestation of signs of concussion in the form of convulsions, similar to epileptic attacks.
- The patient acquires paranoid qualities, as well as neurotic states, when a person is very worried about any reason, worries, and feels fear.
Why does a person lack air or what is hyperventilation syndrome - the causes and treatment of the pathological condition.
Before taking the drug Anafranil - instructions for use, reviews from doctors and patients, effective analogues and other useful information about the medicine.
Rarer complications include psychosis. when a person experiences hallucinations, delusions, and a distortion of the perception of reality.
In some cases, mental disorders can cause acquired dementia, which is characterized by serious shifts in thinking, memory, loss of ability to navigate reality, and apathy.
More often than others, post-concussion syndrome is observed. It can manifest itself any amount of time after the injury with sharp, unbearable headaches, attacks of dizziness, anxiety and sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating on any normal task.
Treatment through psychotherapy rarely helps in this situation; Symptomatic treatment is necessary, but it should be borne in mind that taking powerful painkillers can become more dangerous than the disorder itself and cause dependence on medications.
The consequences of a concussion can be quite serious and varied. Often, irreversible complications appear in extremely severe cases, or when people neglect the damage received and do not adhere to doctor’s orders.
To prevent such consequences, you need to seek help from a specialist in time and strictly follow his instructions:
- bed rest;
- taking necessary medications;
- stop watching TV, reading, listening to music.
This will help you fully recover from damage in a short time and not have irreversible consequences.
What happens with a traumatic brain injury
A mild form of TBI is characterized by one or more of the following symptoms:
- attack of short-term loss of consciousness;
- loss of memory for events immediately before or after the injury;
- any change in mental status at the time of injury;
- focal neurological deficit.
Very often in such cases, the victim looks good outwardly, without realizing that functional problems are developing. Some people suffer from the long-term effects of TBI, known as post-concussion syndrome (traumatic encephalopathy). Persons suffering from this syndrome experience severe headaches, dizziness, decreased performance, weakness, insomnia and intellectual impairment.
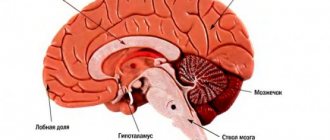
Most traumatic brain injuries result in widespread damage to brain structures. The brainstem, frontal and temporal lobes are particularly vulnerable to local injury from contusions due to their location near bony prominences.
In addition to regulating the basic functions of excitation and inhibition, the brain stem is involved in the processes of attention and short-term memory. Trauma in this area can also lead to autonomic dysfunction: disruptions in metabolism, thermoregulation, respiratory and cardiac activity.
The limbic system helps regulate a person's emotional status. Connected to the limbic system are the temporal lobes, which are involved in many cognitive skills such as memory and language. Damage to the temporal lobes is associated with a number of behavioral disorders.
The frontal lobe almost always suffers from injury due to its large size and location at the front of the skull. The frontal lobe is involved in many cognitive functions and is considered the center of control of emotions and behavior of the individual. Damage to this area can lead to decreased criticality and increased impulsivity.
Restoration of motor skills and functioning of the musculoskeletal system
In the case when, due to a head injury, paralysis or paresis begins to develop, seriously complicating a person’s ability to move independently, he needs the help of a rehabilitation specialist, physiotherapist, or massage therapist. In this situation, specialists can use all sorts of techniques that can help restore the usual tone of the muscles of the limbs, returning the previous sense of balance and balance. In case of such disorders, the massage therapist will massage not only damaged but also healthy limbs for the purpose of prevention.
Exercises prescribed by a specialist in physical therapy and a physiotherapist will help restore the previous coordination of the limbs, relieve the patient of cramps, trembling, and a feeling of weakness in the limbs. You need to understand that restoring such functions is a long and complex process that must be completely under the supervision of doctors. The positive impact of rehabilitation in this case is difficult to overestimate, because it is quite difficult to change something on your own after a TBI.
In situations where rehabilitation measures are started in a timely manner (simultaneously or immediately after treatment), there is a high probability that a patient after a serious injury will be able to move independently and perform simple self-care activities within a few weeks or months. In the absence of the necessary therapeutic actions, a worsening course of disorders may occur, contributing to the complete loss of the ability to walk or move the arms. This stage of pathology develops only in the complete absence of treatment and rehabilitation.
It is important to understand that tremors, numbness, convulsions, paresis, paralysis are all associated with disorders of the nervous system, therefore, in addition to the help of physiotherapists and massage therapists, it is necessary to constantly be in contact with a neuropsychiatrist and psychotherapist
In particularly complex and advanced cases, when traditional exercises and activities do not bring the desired effect, special equipment can be used in rehabilitation centers (for example, the Exart system, etc.). Such units can help activate the patient’s nervous system and muscles.
From the editor: What to do if your child has a headache
Traumatic brain injury and its consequences
Along with disturbances in the movements of arms, legs, and speech, victims with TBI often develop anxiety states that require timely treatment. In recent years, special attention has been paid to improving the diagnosis and treatment of conditions that arise after stressful situations, including after road traffic accidents. This disorder develops after stress, after several weeks or months (rarely more than 6 months), and includes increased anxiety, excitability, decreased memory, attention, and deterioration in performance.
It is known that among people who have suffered a mild TBI, up to 40% have reactions to stressful situations that interfere with their life and work. Usually in such cases, the arms and legs work normally, speech and memory are preserved, and there are no fractures of the skull bones. Examinations by a traumatologist and neurologist do not reveal significant deviations from the norm; It would seem that everything happened without serious consequences. However, after a stressful situation (both psychotrauma and TBI), several weeks or months pass, but the person does not feel cheerfulness, joy of life, gets tired easily, becomes anxious, irritable, worries at the slightest reason, for no significant reason, depressed mood, troubled heartbeats, dizziness. Before going to bed, all the events of the day pass before your eyes, anxiety arises, and it is difficult to fall asleep. As a rule, he wakes up exhausted and not rested during the night. Work that was previously easy to cope with becomes hard work, ordinary household chores become an unbearable burden. It becomes unclear what is happening, because, fortunately, the injury was minor. If such complaints arise, you need to contact a clinic physician or neurologist. To treat such patients, sedatives are used.
Typically, therapy begins with herbal preparations. Today, the drug valemidin, which contains tinctures of valerian, motherwort, hawthorn, mint and a small dose of diphenhydramine, is widely used. It has been proven that valemidine has calming, antiallergic properties, relieves spasms, reduces excitation processes in the central nervous system, and improves sleep. Valemidine is prescribed to adults orally, 30-40 drops 3-4 times a day for 30 minutes for 10 days, then a break for a week and repeated courses.
I would like to emphasize that improvement of the condition cannot be achieved only by taking medications; a correct sleep, work and rest regime is necessary. You need pleasant, heart-warming experiences: this is not only a good book, a TV show, communication with friends, but also work in the garden, of course, with reasonable physical activity. To recover from anxiety, you need to look for a reason to smile and laugh. It’s not for nothing that the philosopher Kant said: “Humor is the talent to arbitrarily put oneself in a good mood.”
M.L. Chukhlovina
Variants of the course of traumatic illness.
variants of the course of a traumatic disease may occur:
:
1) regredient
with continued stabilization of clinical symptoms and maximum rehabilitation of the patient; observed mainly in children, young and middle-aged people. In the elderly and elderly, this outcome is rare;
2) relapsing
with periods of decompensation of direct consequences of injury and remissions; reasons – repeated injuries, intoxication, infections, contraindicated working conditions, etc.; there is no direct relationship between the nature, severity of injury, time of decompensation and progression;
3) progressive
with increasing severity of neurological symptoms, mental disorders, manifestation and development of vascular lesions (arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis); vascular manifestations of traumatic disease in 40% of elderly patients significantly aggravate other consequences of TBI.
How to help in the first minutes
First aid is often provided by people who, by chance, find themselves close to the victim. And they are not always health workers. With TBI, however, it should be understood that loss of consciousness can last a very short time and therefore not be recorded. However, in any case, a concussion, as a complication of any (even seemingly mild) head injury, should always be kept in mind and, taking this into account, help the patient.
If a person who has received a TBI does not come to his senses for a long time, he needs to be turned over on his stomach and his head tilted down. This must be done in order to prevent vomit or blood (in case of injuries to the oral cavity) from entering the respiratory tract, which often happens in an unconscious state (absence of cough and swallowing reflexes).
If the patient has signs of impaired respiratory function (there is no breathing), measures should be taken to restore the patency of the airways and, before the ambulance arrives, provide simple artificial ventilation (mouth-to-mouth, mouth-to-nose).
From the editor: Symptoms, characteristics and treatment of tick-borne encephalitis
If the victim has bleeding, it is stopped with the help of an elastic bandage (a soft lining on the wound and a tight bandage), and when the victim is taken to the hospital, the surgeon will suture the wound. It’s worse when there is a suspicion of intracranial bleeding, because its complication is most likely hemorrhage and hematoma, and this is already a surgical treatment.
Due to the fact that a traumatic brain injury can occur in any place that is not necessarily within walking distance of a hospital, I would like to introduce the reader to other methods of primary diagnosis and first aid. In addition, among the witnesses trying to help the patient, there may be people with certain knowledge in medicine (nurse, paramedic, midwife). And here's what they should do:
The first step is to assess the level of consciousness in order to determine, based on the degree of response, the patient’s further condition (improvement or deterioration), and at the same time – psychomotor status, the severity of pain in the head (not excluding other parts of the body), the presence of speech and swallowing disorders; If blood or cerebrospinal fluid leaks from the nostrils or ears, assume a fracture of the base of the skull; It is very important to pay attention to the victim’s pupils (dilated? different sizes? how do they react to light? strabismus?) and report the results of your observations to the doctor to the arriving ambulance team; You should not ignore such routine activities as determining the color of the skin, measuring pulse, respiratory rate, body temperature and blood pressure (if possible).
With TBI, any part of the brain can suffer, and the severity of one or another neurological symptoms depends on the location of the lesion, for example:
- A damaged area of the cerebral cortex will make any movement impossible;
- If the sensitive cortex is damaged, sensitivity will be lost (all types);
- Damage to the frontal lobe cortex will lead to a disorder of higher mental activity;
- The occipital lobes will no longer control vision if their cortex is damaged;
- Injuries to the cortex of the parietal lobes will create problems with speech, hearing and memory.
In addition, we should not forget that cranial nerves can also be injured and give symptoms depending on which area is affected. And also keep in mind fractures and dislocations of the lower jaw, which, in the absence of consciousness, press the tongue against the back wall of the pharynx, thereby creating a barrier to the air flowing into the trachea and then into the lungs. To restore the passage of air, it is necessary to push the lower jaw forward, placing your fingers behind its corners
In addition, the injury can also be combined, that is, with a TBI, other organs can be damaged at the same time, therefore, a person who has received a head injury and is in an unconscious state must be treated with extreme care and caution
And one more important point when providing first aid: you need to remember about the complications of a TBI, even if at first glance it seemed mild. Bleeding into the cranial cavity or increasing cerebral edema increases intracranial pressure and can lead to compression of the brain (loss of consciousness, tachycardia, increased body temperature) and irritation of the brain (loss of consciousness, psychomotor agitation, inappropriate behavior, obscene language). However, let's hope that by that time the ambulance will have already arrived at the scene and quickly taken the victim to the hospital, where he will receive proper treatment.
Prices for services *
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with a neurologist, MD/Professor | 8250 rub. |
| Appointment and consultation with a neurologist, a specialist in cognitive impairment | 5150 rub. |
| Initial consultation with a physical therapy doctor | 3600 rub. |
| Consultation with a physical therapy doctor, repeated | 2900 rub. |
| Consultation with a physical therapy doctor, Ph.D., primary | 5150 rub. |
| Consultation with a physical therapy doctor, Ph.D., repeated | 3600 rub. |
| Initial consultation with a physiotherapist | 3600 rub. |
| Consultation with a physiotherapist, repeated | 2900 rub. |
| Consultation with a speech therapist-speech pathologist, primary (including an initial speech therapy examination and development of a rehabilitation training program) | 6700 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a psychotherapist | 6000 rub. |
| Individual lesson with a neuropsychologist-neurodefectologist as part of a comprehensive program | 3410 rub. |
| Advanced Neuropsychological Testing | 5665 rub. |
| Neuropsychological testing | 3960 rub. |
| Group clinical and psychological counseling (up to 30 minutes) | 4000 rub. |
| Family clinical and psychological counseling (up to 30 minutes) | 5000 rub. |
| Comprehensive speech therapist session using hardware techniques | 5500 rub. |
| Group lesson with speech therapist | 2200 rub. |
| Individual psychological correction (up to 30 min) | 3400 rub. |
| Correctional session with a speech therapist-defectologist (outpatient) | 3800 rub. |
| Individual lesson on psychological social adaptation | 4565 rub. |
| Individual psychological correction | 6820 rub. |
| Cognitive training session (up to 30 minutes) | 3410 rub. |
| Cognitive training session (up to 60 minutes) | 4950 rub. |
| Individual lesson on restoration of speech functions | 4565 rub. |
| Correctional lesson with a speech therapist-defectologist (30 min) | 3410 rub. |
| Speech therapy examination | 3410 rub. |
| Lymphatic drainage manual massage | 5500 rub. |
| Acupuncture cupping massage | 1705 rub. |
| Therapeutic massage as part of a comprehensive program | 3410 rub. |
| Therapeutic massage of one anatomical area (up to 15 minutes) | 2200 rub. |
| Acupuncture session | 4290 rub. |
| One zone massage (20 min) STAFF ONLY | 1000 rub. |
| Individual kinesiotherapy session as part of a comprehensive program (up to 30 minutes) | 2750 rub. |
| Robotic mechanotherapy as part of a comprehensive program (up to 30 minutes) | 2750 rub. |
| Individual lesson on restoring walking function using an exoskeleton | 5390 rub. |
| Individual kinesiotherapy session (up to 30 minutes) | 2750 rub. |
| Individual kinesiotherapy session (outpatient) | 3850 rub. |
| Individual lesson on the Exart suspension system, 30 min. | 3850 rub. |
| Robotic mechanotherapy, incl. with biofeedback (up to 30 minutes) | 2750 rub. |
| Individual occupational therapy session (up to 30 minutes) | 2750 rub. |
| Individual lesson on a vertical machine with walking simulation (up to 30 minutes) | 3850 rub. |
| Individual kinesiotherapy session using the suspended unloading system Biodex Free Step | 3300 rub. |
| Kinesio taping of one zone (with the cost of the tape) | 1650 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS, 10 days | 148390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS, 14 days | 181390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS, 30 days | RUR 346,390 |
| Medical support during therapy for DMT during a day hospital | 15,000 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE, 10 days | 153890 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE, 14 days | 192390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE, 30 days | RUR 379,390 |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program PARKINSON'S DISEASE, 10 days | 137390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program PARKINSON'S DISEASE, 14 days | 175890 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program PARKINSON'S DISEASE, 30 days | RUR 340,890 |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program STROKE / TBI, 10 days | 148390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program STROKE / TBI, 14 days | 181390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program STROKE / TBI, 30 days | RUB 357,390 |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program SPINAL INJURY, 10 days | 159390 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program SPINAL INJURY, 14 days | 208890 rub. |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program SPINAL INJURY, 30 days | 401390 rub. |
What determines the severity of TBI and its types?
All, including long-term types of consequences of traumatic brain injury, are subject to many factors:
- Nature of injury. The stronger and deeper it is, the greater the likelihood of complications and, as a result, long-term treatment.
- Patient's age. The younger the body, the easier it is for it to cope with the injuries received.
- Speed of medical care. The sooner the victim is shown to a doctor and the stage of treatment begins, the easier it will be for him to recover.
As already mentioned, there are mild, moderate and severe forms of damage. According to statistics, there are almost no complications with minor injuries in young people aged 20–25 years.
Consequences in mild form
A mild form of head trauma is the most favorable option of all existing ones. Treatment usually does not take much time, and patients recover quickly. All complications are reversible, and symptoms are either early (acute) or last a short time. The following signs can be noted here:
- dizziness and headaches;
- profuse sweating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- irritability and sleep disturbance;
- weakness and fatigue.
Typically, therapy, after which the patient returns to normal life, takes 2 to 4 weeks.
Consequences in moderate form
Moderate severity is a more serious reason for concern about the patient’s health. Most often, such conditions are recorded with partial brain damage, severe bruise or fracture of the base of the skull. The clinical picture can last for quite a long time and includes symptoms:
- speech impairment or partial loss of vision;
- problems with the cardiovascular system, or more precisely with heart rhythm;
- mental disorders;
- paralysis of the cervical muscles;
- seizures;
- amnesia.
Rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury can take from 1 month to six months.
Consequences in severe form
Severe injuries are the most dangerous and are the most likely to cause death. Most often, this type of injury is recorded after open skull fractures, severe brain contusions or compression, hemorrhages, etc. The most common type of complication after severe TBI is coma.
From the editor: How neuralgia manifests itself and is treated in children
According to statistics, every second person in severe cases will experience the following types of consequences:
- Partial or complete disability. In case of partial disability, the ability to work is lost, but self-care skills are retained, mental and neurological disorders are present (incomplete paralysis, psychosis, movement disorders). With complete disability, the patient requires constant care.
- Coma of varying degrees of manifestation and depth. Coma due to traumatic brain injury can last from several hours to several months or years. At this time, the patient is on artificial life support devices or his organs are working independently.
- Death.
Also, even the most effective treatment and a favorable outcome of the measures taken necessarily entail the appearance of the following signs:
- problems with vision, speech or hearing;
- abnormal heart rhythm or breathing;
- epilepsy;
- seizures;
- partial amnesia;
- personality and mental disorder.
They can be combined and appear immediately after a head injury or years later.
It is impossible to give an accurate assessment of the patient’s recovery, because each organism is individual, and there are multiple examples of this. If in one case, even with severe injuries, patients endured rehabilitation with resilience and returned to normal life, then in other situations, even a mild head injury did not have the best effect on the neurological status and health in general. In any case, rehabilitation and psychological support play an important role in cases of traumatic brain injury.
With such an injury, a possible complication) is damage to the skull and soft structures of the brain: blood vessels, cranial nerves, meninges.
Neurosurgery distinguishes open brain injury, when the cranial cavity has communication with the external environment, and closed one. Patients often complain of prolonged loss of consciousness and depression due to traumatic brain injury. Coma gives a signal that the patient's condition is critical and urgent medical intervention is required. With this injury, a coma indicates a general deterioration in brain activity.
Rehabilitation of TBI
Treatment of traumatic brain injury begins already at the stage when first medical aid is provided, and already in the hospital the patient is provided with the second stage of medical care, and is also offered rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury received in one way or another. The initial examination is carried out with special attention, especially if the patient has lost consciousness. In this case, the patient is immediately sent to the hospital to conduct the necessary studies aimed at making a diagnosis and preventing the occurrence of life-threatening and health-threatening consequences. Depending on the results of the study, surgical intervention may be recommended or it may be determined that there is no need for it. All prescriptions are based on the type, nature and severity of the existing TBI.
Moderate bruise GM
The clinical picture is characterized by a loss of consciousness for a longer period (up to several hours). The patient experiences repeated vomiting, intense headache, more severe amnesia and mental disorders. An increase in blood pressure and body temperature, increased respiration, pulse, and meningeal signs are detected. Focal neurological symptoms appear, the manifestations of which depend on the location of the injury. These may be speech disorders, motor disorders (paresis), oculomotor disorders, etc. The condition improves within 3-5 weeks, focal symptoms may persist longer. During examination, damage to the skull bones and subarachnoid hemorrhage are often diagnosed. The latter develops as a result of rupture of the vessels of the pia mater, and sometimes rupture of the cerebral sinuses. Its manifestations can occur acutely (severe headache, agitation, delirium, disorientation, back pain and radicular symptoms) or increase gradually.
FEATURES OF RECOVERY AFTER CRANIO BRAIN INJURIES
The patient’s well-being and prognosis after TBI depend on the mechanism of injury and the presence of other disorders in the body. Therefore, an integrated and individual approach is required when selecting a recovery program.
Possible disorders after TBI:
1. Violation of musculoskeletal functions and motor skills.
The patient experiences spontaneous contraction and spasticity of muscles, tremors of the limbs, paralysis, loss of sensitivity, impaired coordination of movement, etc.
2. Impaired cognitive functions.
- hearing impairment. May occur due to rupture of the eardrum and accumulation of blood in the middle ear;
- amnesia – loss of memory and inability to recall memories;
- dementia, confusion, mental decline;
- blurred vision.
3. Bulbar disorders - impaired swallowing and speech. The patient speaks slowly, sometimes pronouncing a bunch of words instead of meaningful phrases. There may be difficulty understanding speech and remembering words.
4. Psychoorganic disorders: problems with the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
5. Headache and dizziness. These symptoms can accompany even mild TBIs.
6. Changes in psychological state (anxiety, insomnia, apathy and depression).
Prices for rehabilitation after injuries *
| Name of service | Price |
| 8250 rub. | |
| 5150 rub. | |
| 3600 rub. | |
| 2900 rub. | |
| 5150 rub. | |
| 3600 rub. | |
| 3600 rub. | |
| 2900 rub. | |
| 6700 rub. | |
| 6000 rub. | |
| 3410 rub. | |
| 5665 rub. | |
| 3960 rub. | |
| 4000 rub. | |
| 5000 rub. | |
| 5500 rub. | |
| 2200 rub. | |
| 3400 rub. | |
| 3800 rub. | |
| 4565 rub. | |
| 6820 rub. | |
| 3410 rub. | |
| 4950 rub. | |
| 4565 rub. | |
| 3410 rub. | |
| 3410 rub. | |
| 5500 rub. | |
| 1705 rub. | |
| 3410 rub. | |
| 2200 rub. | |
| 4290 rub. | |
| 1000 rub. | |
| 2750 rub. | |
| 2750 rub. | |
| 5390 rub. | |
| 2750 rub. | |
| 3850 rub. | |
| 3850 rub. | |
| 2750 rub. | |
| 2750 rub. | |
| 3850 rub. | |
| 3300 rub. | |
| 1650 rub. | |
| 148390 rub. | |
| 181390 rub. | |
| RUR 346,390 | |
| 15,000 rub. | |
| 153890 rub. | |
| 192390 rub. | |
| RUR 379,390 | |
| 137390 rub. | |
| 175890 rub. | |
| RUR 340,890 | |
| 148390 rub. | |
| 181390 rub. | |
| RUB 357,390 | |
| 159390 rub. | |
| 208890 rub. | |
| 401390 rub. |
Sequence of actions for traumatic brain injury
Emergency care for traumatic brain injuries involves contacting a doctor. You will need to call an ambulance even if it seems that the person is practically unharmed. With brain injuries, symptoms often do not appear immediately.
The algorithm of actions before the arrival of the medical team includes several steps:
- Place the patient on a flat surface. It must be tough;
- determine if other lesions are present and examine the head to determine what type of injury has occurred. After the ambulance arrives, provide information;
- check whether breathing is present, whether the heartbeat has weakened, as well as the pulse;
- if the victim does not regain consciousness, he is placed not on his back, but on his side;
The victim is placed on his side and cold is applied. - if there is an open injury, the affected area is treated with antiseptics and a bandage is also used. It will close the wound from infections and reduce the risk of developing inflammatory processes;
- use cold compresses to prevent brain swelling;
- The neck should not move, so keep it still.
Determine whether there is a pulse, heartbeat, breathing. If they are absent, resuscitation assistance must be provided. Indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration are used. Do not leave the person until medical help arrives.
Immobilize the neck and be careful that the baby does not choke on vomit. Assess the child's condition
Pay attention to whether he is conscious, and if not, how long the fainting lasts. Other symptoms of a possible concussion or bruise are also important: nausea, dizziness, memory loss. Monitor your child's condition if you have not sought medical help. Quite often, the consequences of injury appear after 1–2 days.
Assess the child's condition
Pay attention to whether he is conscious, and if not, how long the fainting lasts. Other symptoms of a possible concussion or bruise are also important - nausea, dizziness, memory loss
Monitor your child's condition if you have not sought medical help. Quite often, the consequences of the injury appear after 1–2 days.
If you contact the doctors, before they arrive, place the victim on a flat, not soft surface
Immobilize the neck and be careful that the baby does not choke on vomit. If he faints, turn him over on his side.
In general, the algorithm of actions for damage to the meninges in a child is almost identical to those used for damage to adults.
Knowledge of the algorithm for providing emergency care for traumatic brain injury will prevent consequences that can lead to a decrease in the quality of life or death of a person.
Help for TBI should begin with calling specially trained medical personnel.
First aid is carried out in a certain sequence.
- Call a doctor.
- Providing first aid for traumatic brain injury begins with determining the level of consciousness. The person needs to be awakened.
- Examine the patient's injury. Check for bleeding.
- Determination of heart rate and respiration. The heartbeat may slow down or stop completely. If it is absent, cardiac massage begins. Removal of foreign bodies when the airways are filled.
- First aid for a traumatic brain injury includes applying a bandage.
- If there is no spinal injury, the patient is placed on his side to prevent suffocation. If there is a spinal injury, the patient is left on his back.
- Apply cold to the site of a closed head injury.
From the editor: In what cases is brain bypass performed?
Despite the fact that the patient feels fine after the injury, it is necessary to check his health with a doctor. Damage can be hidden and appear after a few hours or even 1-2 days. Only studies in the form of MRI and CT can diagnose internal injuries.
When blood vessels rupture, blood gradually accumulates, reaching a maximum peak after a few hours or days. Lack of first aid provided by a doctor can result in the death of the patient.
How to recover from a traumatic brain injury?
Recovery from a traumatic brain injury includes two main components – intensive care and rehabilitation. In this case, as a rule, after a course of intensive therapy, continued treatment in the form of gentle therapy is required. This type of treatment essentially forms part of a rehabilitation course. The main goal of intensive care is to prevent serious complications of injury, such as edema, circulatory disorders and cerebral hypoxia, impaired respiratory function and complications from the cardiovascular system. After the main dangers have been eliminated, the turn of rehabilitation begins, the task of which is to maximize the preservation of mental and physical activity and its gradual restoration.
Unfortunately, in most cases of traumatic brain injury, some functions and skills are impaired and partially or completely lost. In particular, problems with speech may occur. A person cannot cope with this problem on his own; in this he needs the help of a specialist - a speech therapist-aphasiologist.
To restore physical activity and performance, rehabilitation centers use specialized complexes such as Erigo. This computerized system allows you to effectively combine traditional verticalization with intensive movement therapy. To do this, the patient's legs are driven by actuators connected to a computer. The movements created in the legs imitate the movements of walking, which helps restore lost walking skills not only in case of traumatic brain injury, but also in case of stroke. In addition, this technique improves the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, prevents and helps eliminate secondary complications after traumatic brain injury associated with prolonged immobility (including muscle atrophy).
Successful recovery from traumatic brain injury is impossible without therapeutic measures aimed at improving blood supply and brain function. At the same time, the main task of rehabilitation is to preserve the surviving brain functions and create new abilities to replace the lost ones in order to return a person to normal life and social activity.
Psychological assistance is of great importance in this, along with drug treatment, traditional methods of physiotherapy, reflexology, manual therapy, as well as such modern methods as myostimulation, PNF therapy and ozone therapy. It means not just moral support from relatives and loved ones, but professional assistance from a psychotherapist in order to maximally motivate the patient to recover, prevent or overcome post-traumatic depression, create a positive attitude and accelerate social adaptation.
With so many components, it becomes obvious that truly effective, comprehensive rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury can only be carried out in a specialized hospital on the basis of an individual course and with the involvement of a number of specialized specialists.
Treatment
After an injury, patients receive first aid at the scene of the accident by an emergency medical team. If the patient is unconscious, he is turned on his side or face down. First aid measures are aimed at preventing aspiration of vomit and clearing the airways, stopping bleeding. Such patients are required to be hospitalized in a hospital.
The nature and scope of treatment is determined by the condition and age of the victim, the severity of edema of brain tissue, liquor hypertension, impaired cerebral hemodynamics, etc.
All patients with a bruise of brain tissue are advised to rest, bed rest for a period of 7 days to 2 weeks, constant medical supervision is required. Drug therapy includes the prescription of the following medications:
- analgesics (ibuprofen, analgin, ketorol);
- antiemetic drugs (metoclopramide, domperidone);
- sedatives (phenazepam, Relanium, adaptol);
- with severe agitation - haloperidol, sodium hydroxybutyrate;
- diuretics (furosemide, diacarb, manitol);
- antihistamines (tavegil, suprastin);
- hemostatic agents for hemorrhage (dicinone, etamsylate);
- Medicines that improve blood circulation in brain tissue (sermion, vinpocetine);
- metabolic agents (piracetam, cerebrolysin);
- nootropic drugs (zncephabol, nootropil);
- B vitamins (milgamma, neirovitan).
To sanitize the cerebrospinal fluid and reduce its pressure, a therapeutic lumbar puncture is used.
Severe bruises of the brain require resuscitation and intensive care.
Surgical treatment is indicated for large areas of tissue crushing and the absence of effect from conservative treatment.
Measures for caring for patients with bruises of the brain consist of the prevention of bedsores, pneumonia, and passive exercises to prevent contractures.
Patients who have suffered a brain injury are subject to long-term follow-up. During the recovery period, they are recommended to take courses of vascular therapy, exercise therapy, physiotherapeutic and sanatorium-resort treatment. The latter can be prescribed several months after the injury in the absence of pronounced motor and mental disorders. In the presence of gross residual defects, the issue of the patient’s ability to work is resolved.
Prevention of complications, rehabilitation
Only timely treatment can reduce the risk of negative consequences after a head injury. First aid is usually provided by medical personnel. But people who were close to the victim at the time of his injury can also help. You need to do the following:
- Turn the person over to a position in which the likelihood of hypoxia and asphyxia is minimal. If the victim is conscious, you should turn him on his back. Otherwise, you need to lay it on its side.
- Treat the wound with water or hydrogen peroxide, apply bandages and a bandage to it: this will reduce swelling and the risk of developing infectious complications with an open head injury.
- If signs of asphyxia, difficulty breathing, or heart rhythm disturbances appear, perform cardiopulmonary massage and provide the patient with access to air.
- Stop accompanying bleeding, treat other damaged areas of the body (if any).
- Wait for the ambulance to arrive.
Editorial: How to relieve migraine headaches
Treatment of head injuries is carried out exclusively in a hospital, under the strict supervision of a doctor. Depending on the type and severity of the pathology, drug therapy or surgical intervention is used. The following groups of drugs may be prescribed:
- analgesics: Baralgin, Analgin;
- corticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Metipred;
- sedatives: Valocordin, Valerian;
- nootropics: Glycine, Phenotropil;
- anticonvulsants: Seduxen, Diphenin.
Typically, a patient's condition after an injury improves over time. But the success and duration of recovery depends on the measures taken during the rehabilitation period. Lessons from the following specialists can return the victim to normal life:
- occupational therapist. Works on renewing self-care skills: moving around the apartment, driving a car as a passenger and driver;
- neurologist. Deals with issues of correction of neurological disorders (decides how to restore the sense of smell, reduce seizures and what to do if you constantly have a headache after suffering an injury);
- speech therapist. Helps improve diction, cope with the problem of slurred speech, restores communication skills;
- physiotherapist. Carries out pain correction: prescribes procedures to reduce headaches after head injury;
- kinesitherapist. Its main task is to restore the functions of the musculoskeletal system;
- psychologist, psychiatrist. Help eliminate mental disorders due to brain injuries.
The first diagnosis is in doubt
At the first examination in the hospital, the diagnosis of brain contusion without a question mark is not given to the victim. The patient is examined to find abrasions, wounds, bruises, if any, and also to determine whether there are any fractures of the skull bones (bleeding from the ears or nostrils), shoulder girdle, lower extremities, pelvis or spine, whether internal organs are damaged, after all, you should always think that the injury can be combined. The diagnosis is initially preliminary, where the main assessment criterion is the patient’s consciousness, his behavior and the state of his reflexes.
For example, symptoms of a brain contusion that can be seen when examining the victim may look like this:
- Loss of consciousness (depending on the severity) may last for several minutes, or may progress to another state. The most likely transition is to stupor, when it is not possible to talk with the patient, but he reacts to pain with grimaces on his face, reflecting suffering, defensive movements, groaning, or in a coma with a complete lack of consciousness, immobility, loss of swallowing reflexes - the patient will come out of it ( or will it not work out?) after many days;
- Impaired consciousness and psychomotor agitation are signs of brain damage that cannot be ignored if this option occurs: the patient groans, is agitated, grabs his head with his hands, behaves inappropriately, insults health workers, resists diagnostic measures;
- With preserved consciousness and an adequate reaction to the environment, the patient, on the contrary, is quiet and passive, tries not to move, is reluctant to make contact, tries to answer questions in monosyllables (“yes”, “no”), he is irritated by loud sounds and lights. The patient complains in a quiet voice of dizziness, unbearable headache, nausea, and asks for a container that can be used for vomiting. When a condition such as somnolence occurs, the patient is overcome by irresistible drowsiness and then contact with him is difficult due to the fact that he has poor control of the environment, constantly falls asleep and only persistent repetition of questions forces him to squeeze out a monosyllabic answer;
- With a brain contusion, neurological symptoms appear with varying degrees of severity: floating eyeballs, decreased reaction of the pupils to light, nystagmus (twitching of the eyeball when moving the eyes to the side), paresis of facial muscles, difference in strength and range of movements in the limbs of the left and right side of the body , paralysis and cramps in the limbs. It should be borne in mind that neurological disorders can be quite variable and transient in nature, moreover, they are recorded with preserved consciousness, and impaired verbal contact, swelling of the face and deformation of the bones of the facial skeleton, and injuries to the extremities complicate a neurological examination;
- Disorders of respiratory function (rhythm and frequency of respiratory movements), changes in body temperature and cardiac disturbances (heart rate, heart rhythm, blood pressure) can be quite severe in severe cases;
- Meningeal symptoms are more typical for bruises of moderate severity and severe cases and are signs of a serious complication - subarachnoid hemorrhage. Although in old people meningeal signs appear every once in a while, in children they may be completely absent.
However, the statement that the victim has a brain contusion can only appear after a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- Craniography (x-ray of the skull bones);
- Echoencephalography - EchoEG (ultrasound examination of the brain);
- Electroencephalography (EEG);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Lumbar (spinal) puncture.
By approaching the examination of a patient with TBI very carefully, one can judge the severity of the traumatic brain injury, and by carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures using tools and equipment, one can establish a diagnosis of a concussion of the brain, a brain contusion, or, God forbid, something even worse serious.
Types of TBI
This injury has a very broad classification depending on the nature and method of injury received by the patient:
- mild, moderate and severe form;
- isolated, combined (with damage to other organs) and combined (in the presence of various traumatic factors);
- open (with damage to the aponeurosis) or closed (the aponeurosis is not damaged).
In clinical forms, TBI can be expressed:
- head concussion;
- head contusion;
- compression of the brain;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- fracture of the skull bones;
- diffuse axonal damage.
A combination of types of traumatic brain injury is also possible, so contacting a specialist to obtain an accurate diagnosis is simply necessary. In some cases, there are patients who are indicated for recovery after TBI.